by Tony Wikrent
Strategic Political Economy
What is the deep state? (YouTube video)
(Jeffrey Sachs, John Mearsheimer, YouTube, via Thomas Neuburger, God’s Spies, 09-20-2024]
This video segment is taken from a symposium at which Sach and Mearsheimer offered their views on U.S. foreign policy. The whole thing is worth a listen, but I’ve cued this to start at the point where the question, “What is the deep state?” is asked and answered.
Note: The answer relates to foreign policy only, not the broader question of “Does the Establishment State try to influence domestic politics?”
“Sachs: My experience … is that there’s a deeply entrained foreign policy. It has been in place in my interpretation for many decades. But arguably a variant of it has been in place since 1992. I got to watch some of it early on because I was an adviser to Gorbachev and I was an adviser to Yeltsin, and so I saw early makings of this though I didn’t fully understand it except in retrospect.
“But that policy has been mostly in place pretty consistently for 30 years, and it didn’t really matter whether it was Bush Senior, whether it was Clinton, whether it was Bush Jr., whether it was Obama, whether it was Trump.
“After all, who did Trump hire? He hired John Bolton. Well, duh, pretty deep state. That was the end of … they told, you know, he [Bolton] explained this is the way it is. And by the way, Bolton explained also in his memoirs, when Trump didn’t agree we figured out ways to trick him basically.”
….
“MEARSHEIMER: When we talk about the ‘Deep State,’ we’re really talking about the Administrative State. It is very important to understand that starting in the late 19th and early 20th century, given developments in the American economy, it was imperative that we develop — and this is true of all Western countries — a very powerful central state that could ‘run the country.’ And over time, that state has grown in power.
“Since World War Two, the United States has been involved in every nook and cranny of the world, fighting wars here, there, and everywhere. And to do that, you need a very powerful administrative state that can help manage that foreign policy. But in the process, what happens is you get all of these high-level, middle-level, and low-level bureaucrats who become established in positions in the Pentagon, the State Department, and the intelligence community — you name it. And they end up having a vested interest in pursuing a particular foreign policy.
“That particular foreign policy that they like to pursue is the one the Democrats and the Republicans are pushing. That’s why we talk about tweedle-dee and tweedle-dum with regard to the two parties. You could throw in the deep state as being on the same page as those other two institutions….”
[TW: This is an important glimpse into the thinking of USA ruling elites. But just as important as what was said, is what was not said. There was no discussion of cooperation between nations on solving global problems, in line with what I have identified as a core principle of civic republicanism: one major role of government is to encourage people to do good by increasing humanity’s power over nature. There was no mention whatsoever of climate change, which absolutely will require global cooperation, probably on an unprecedented level. How about an international effort to help Mexico build a second Panama Canal? Or a crossing of the straits of Gibraltar, now considered an insurmountable engineering challenge. Wouldn’t it be much better to focus energies and resources on such projects?
[Increasing humanity’s power over nature: that’s what sewer systems and water distribution systems did — projects which are probably the single largest factor in tripling average human life expectancy in the past three centuries. Sewer systems and water distribution systems are primary examples of increasing humanity’s power over nature. Not just power over flows of water, but power over the spread of bacteria and viruses.
[The “realism” discussed by Sachs and Mearsheimer emphasizes competition — just like neoliberal “free market” economics. The real way to avoid nuclear war is to emphasize the cooperation of the human family in solving the problems we call face. The old paradigms of thought must be banished and replaced. For example, the idea that economics is about how “society allocates scarce resources” (taught in all “classical economics” texts and courses in the West), must be replaced by the understanding of civic republican political economy that the foremost economic task of any society is to overcome scarcity and provide abundance by increasing the power of humanity to understand and prudently control natural resources, then to distribute that abundance equitably to all of humanity. One major international cooperative project that cries out for attention and support is to build sewer systems and water distribution systems throughout the entire world, most especially areas in Africa and South American which do not now have them. There should not be any people anywhere on the globe who are forced to spend large parts of their day filling the basic need of securing enough clean water to drink, bathe, and cook.
[Eight years ago, China proposed an international $50 trillion project to build an electric power grid to bring solar and wind generated electricity from the polar and equatorial regions of the world, to the more populated regions that use the electricity. It is a great strategic mistake to ignore such proposals. ]
Global power shift
China leads world in 57 of 64 critical technologies; up from 3 just 20 years ago
[Hacker News, via Naked Capitalism 09-21-2024]
ASPI’s two-decade Critical Technology Tracker
[ASPI, via Naked Capitalism 09-21-2024]

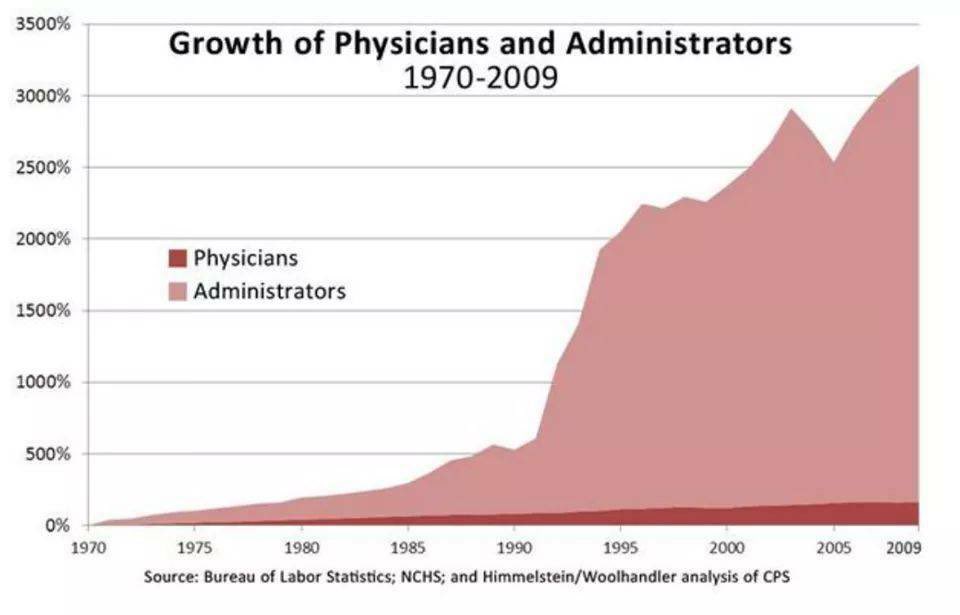
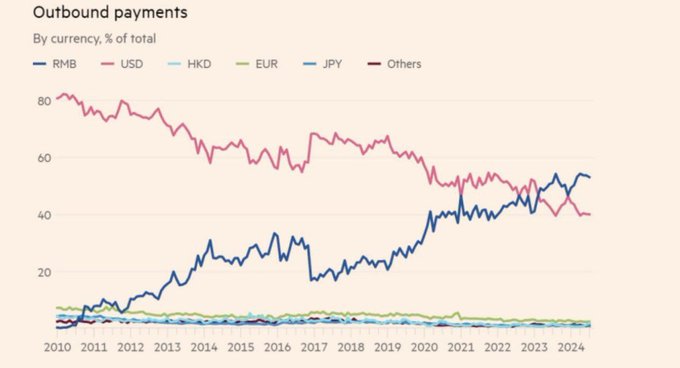
There is an underlying dynamic of solidarity and surplus that seldom gets the attention it deserves.
Ancient Greece at the end of the of the Bronze Age participated in the famous but mysterious collapse and entered a Dark Age of significantly diminished population, political organization and culture. They emerged beginning around 800 BCE, apparently with a new set of technologies, politics and agriculture and trade that generated surplus. People were healthy and well-fed (comparatively). Greece experienced a population boom, increasing in numbers roughly ten times over 400 years and a critical part of the competition among city-states was to found colonies. It wasn’t just Greece, Phoenicia and the Etruscans and others were involved.
Technological innovation is not a merely moral phenomenon; it is a matters of surplus and numbers. There must be a surplus to feed an artisan class and trade and a differentiation of labor.
The surplus that fed the urban civilization that Rome engineered diminished with soil erosion. The extraction of the tradeable surplus from a slave class on the great latifundia was inefficient and self-defeating on many levels, undermining the economic foundation of an urban civilization. People at the bottom of the system were unhealthy. Famines and plagues ensued. Trade declined with falling division of labor in a dimishing artisanal class, compounding the effects of declining agricultural surplus.
The rise of China followed on the creation of enormous agricultural surplus to feed vast armies and an urban civilization with a huge artisanal population, with trade driving deep division of labor and technological inventiveness. The surplus originated in vast hydraulic projects and the elaboration three-crop rice production.
There would be no social barrier in China to ever more labor intensive agriculture: more and more hands in the fields until the extraction of surplus was choked off by congestion losses. By 1500, Chinese peasants could barely feed themselves. Ordinary people were physically weak. The cities were huge, but represented only single-digit percentages of total population.
Europe recovering from the Dark Ages that followed the collapse of Rome saw a revival of surplus, especially after iron plows turned the heavy but fertile soils of Northern Europe and dug deeper in the south. But, the congestion losses of too many hands in the fields showed quickly too and the flowering of the High Middle Ages ended in overpopulation and the Black Death, which was driven as much by imminent famine as rats and fleas.
The contrasting aftermaths of the Plague of Justinian and the Black Death — two, long series of bubonic plagues sweeping thru Europe is worth contemplating. One destroyed a civilization and the other seemed to spark a new civilization.
Agricultural surplus feeding a growth of artisanal production and merchant trade, but being choked off by congestion and extractive oppression is a recurrent dynamic. It underlies the peculiar history of rivalry between England and France. France, with the greatest agricultural potential in western Europe, occupying an extensive well-watered plain, had a vastly greater population than England thruout the Middle Ages and well into the 19th century. But, France became overpopulated. Famine and hunger drove the French Revolution when bad weather triggered bad harvests that threatened the surplus that fed Paris.
England’s ability to feed its industrializing cities was a near-run thing in the 18th and 19th centuries. The additional surplus generated by the British Agricultural Revolution was a paltry thing and Ireland was kept on the edge of famine by overpopulation until pushed over the edge.
The productive often desperate competition that Ian draws attention to has a multi-path causal relation to the generation and/or extraction of surplus. That surplus may originate in accidents, be managed or neglected by elites and be extinguished without intention.