 Economics is largely a worthless discipline. Its axioms, like humans being rational utility maximizers, are simply wrong and everything built on top of them is thus flawed. It reminds me of pre-Copernican astronomy, which was based on the idea that the sun and planets revolved around the Earth. The difference is that pre-Copernican astronomy more or less worked and economics mostly doesn’t.
Economics is largely a worthless discipline. Its axioms, like humans being rational utility maximizers, are simply wrong and everything built on top of them is thus flawed. It reminds me of pre-Copernican astronomy, which was based on the idea that the sun and planets revolved around the Earth. The difference is that pre-Copernican astronomy more or less worked and economics mostly doesn’t.
But there are insights in economics, and there’s a cluster around free, or rather, competitive markets. In order for competitive markets to work:
- There must be lots of buyers and sellers, so no one has pricing or buying power.
- There must be no significant barriers to entry. If you can’t start a new business doing whatever it is, market incumbents can jack up prices. Barriers to entry are both legal and technical: if there’s no availability of whatever is needed to make the product, that’s a barrier to entry.
- Products must be roughly the same. If one producer is able to produce much better products, then people will buy that. This means, in effect, that intellectual property laws must be open, or people won’t be able to produce roughly equal goods.
- Collusion in setting prices cannot be allowed, nor can special deals like larger buyers getting better prices. (A large supermarket which pays lower prices will drive smaller ones out of business till there are only a few major supermarket firms left.)
Now the problem with competitive markets, from the point of view of capitalists, is that they keep profits low. If you start jacking up your prices, your competitors will get the business, since the products are about the same and since other firms can easily enter the business.
Competitive markets lead to fast innovation and low prices, with any high profit periods due to innovation lasting only as long as it takes for others to reproduce the new product. If you want high profits over a long time period you have to keep innovating, you can’t make essentially the same product forever and expect to make more than average (low) profits.
But business hate competitive markets, exactly because they do make it almost impossible to make high profits over the long term.
So business profs and consultants read the economic literature and said “if we want to make high profits we have to find or create businesses which are not competitive.
Reverse engineering, high profits come to companies which are oligopolies or monopolies so they have pricing power; to companies in industries where there are significant barriers to entry, whether thru intellectual property laws or vertical integration; to companies that have a better product because no one else is allowed to make that product (pharma is great at this); and to businesses which collude on prices. Right now, for example, a lot of landlords subscribe to a software service which sets prices and even keeps rental properties off the market in order to keep rents high.
There are other tricks, of course. Health providers, in general, have an advantage. When someone’s seriously sick they can’t really comparison shop and they’re desperate, they’ll pay whatever they have to save their life or get well.
Another one is network externalities. If everyone’s on one site or a few, then other sites have a hard time competing. Think of Facebook’s suite of sites, or think of Google’s monopoly on search.
When Private Equity and investors who provide seed capital roll up firms or invest in new firms, they’re either looking to liquidate those they buy (PE likes this) or they’re trying to destroy a competitive market so they can charge much more than a competitive market would normally allow.
One of the things which has made China so dynamic is that it has much more competitive markets than America or Europe. There are dozens of EV firms, for example. Tons of drone makers. Multiple space companies. Absolutely massive supply networks where you can buy anything you need to make whatever it is, or get them to make anything new you’ve thought up. IP laws are weaker, and often not enforced, and so on. Where there is market power, the government often steps in either to regulate what firms can charge (in natural monopolies like power distribution, for example) or to prevent the use of that market power to freeze out competitors.
As the US and the West have financialized, they’ve destroyed most of the laws which were in place to keep markets competitive. Eggs, for example, are not high priced primarily because of Avian bird flu, but because there are only a few oligopoly suppliers in the market, and they’re making more money with shortages than they would by providing as many eggs as people really want to buy at lower prices. Those prices would still be profitable, but they would be obscenely high.
Almost all Western industries are now entrenched behind various barriers designed to give them pricing power: to allow them to charge more than they could in a competitive market.
So China, with competitive markets, produces EVs which cost under 20K in many cases. Everything they produce is cheaper than in the West. This isn’t all about barriers and non-competitive markets, but a lot of it is and most of what seems to not be about competitive markets, like needing to pay American workers more, really is. American workers need more money because of high rent, high health care costs, high tuition, high real estate prices and just, in general, high prices. When Chinese show Americans their grocery bills, Americans are startled and some even cry, they are so much cheaper.
So driving up prices deliberately makes US goods in particular, and Western goods in general non-competitive because it jacks up the cost structure.
Matt Stoller, of course, is the premier thinker and activist around this and his BIG column is worth reading regularly.
But the simple takeaway is that your life sucks and the West can’t compete because of non-competitive markets and the regulations which are bad are those which make it non-competitive: horrific IP laws, non enforcement of anti-trust, allowing huge mergers and so on.
If America and the West are ever to be competitive again, we must make markets competitive and where they can’t be, in natural monopolies like energy and water and so on, we must have regulations that directly control prices, as we did in the 50s and 60s, where utilities were basically guaranteed a 5% profit, and forced to reinvest in infrastructure (no California fires because PG&E would rather pay dividends then replace century old power lines and poles).
This isn’t really a hard problem, conceptually. We know how to create competitive markets, and regulate non-competitive markets. We’ve done it before. It is entirely a political issue, because incumbents with tons of money also have tons of political power.
But don’t let anyone spew nonsense like “it’s complicated” or suggest it’s an unsolvable problem, it isn’t.
You get what you pay for. This blog is free to read, but not to produce. If you enjoy the content, donate or subscribe.


 Economics is largely a worthless discipline. Its axioms, like humans being rational utility maximizers, are simply wrong and everything built on top of them is thus flawed. It reminds me of pre-Copernican astronomy, which was based on the idea that the sun and planets revolved around the Earth. The difference is that pre-Copernican astronomy more or less worked and economics mostly doesn’t.
Economics is largely a worthless discipline. Its axioms, like humans being rational utility maximizers, are simply wrong and everything built on top of them is thus flawed. It reminds me of pre-Copernican astronomy, which was based on the idea that the sun and planets revolved around the Earth. The difference is that pre-Copernican astronomy more or less worked and economics mostly doesn’t.
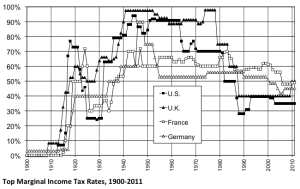
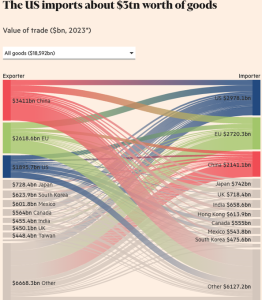 The final part of the economy is what you can get from other nations. Call this the external economy. Does someone else make it, will they sell it to you, can you afford it? Most of the time countries won’t sell other countries nukes, for example, and for much of history countries tried not to sell other countries the knowledge required to make advanced techs. When they didn’t prevent this, they paid big time: Britain was de-facto subjugated by America and America is now losing its Empire.
The final part of the economy is what you can get from other nations. Call this the external economy. Does someone else make it, will they sell it to you, can you afford it? Most of the time countries won’t sell other countries nukes, for example, and for much of history countries tried not to sell other countries the knowledge required to make advanced techs. When they didn’t prevent this, they paid big time: Britain was de-facto subjugated by America and America is now losing its Empire.