That seems most likely to me. China has been stalling out for some time, Japan’s “stimulus” didn’t work, Europe has been suffering under austerity for years (despite some minor good news), the other emerging economies are doing badly, the petro-states have been hammered by the drop in oil prices and now the US job market has fallen off a cliff after a few months of excellent results.
Those results were driven almost entirely by the drop in oil prices, but were unsustainable with most of the rest of the world economy in the doldrums. Low oil prices should be generally good for everyone but oilarchies, but their effect is muted (in comparison to past decades) by the oligarchical and oligopolistic nature of our economy. Put simply, there are too many barriers to entry for new businesses to arise and even lower oil prices don’t put enough money into ordinary people’s hands to create enough new demand for long enough.
In an economy where individual sectors tend to be controlled by a few companies, and where those companies are already awash with money, more money means little; those with pricing power will simply take it away and add it to the stockpiles of money they already aren’t using for anything productive.
The standard solution to the situation we’re in now would either be to implement very high corporate and individual marginal taxation (if private actors won’t spend, take the money from them) and/or to break up oligopolies and/or to heavily regulate them so that they aren’t sopping up all the excess cash in the economy. (Why are app stores still allowed to take 30%, for instance?)
Since we refuse to do any of those things, and since we only print money to give to rich people and corporations (thus pooling money at the top, doing little for widespread demand), the western economy (which includes Japan) remains stagnant. You may get a few good months here and there, but that’s all you’re going to get.
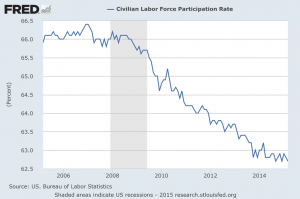
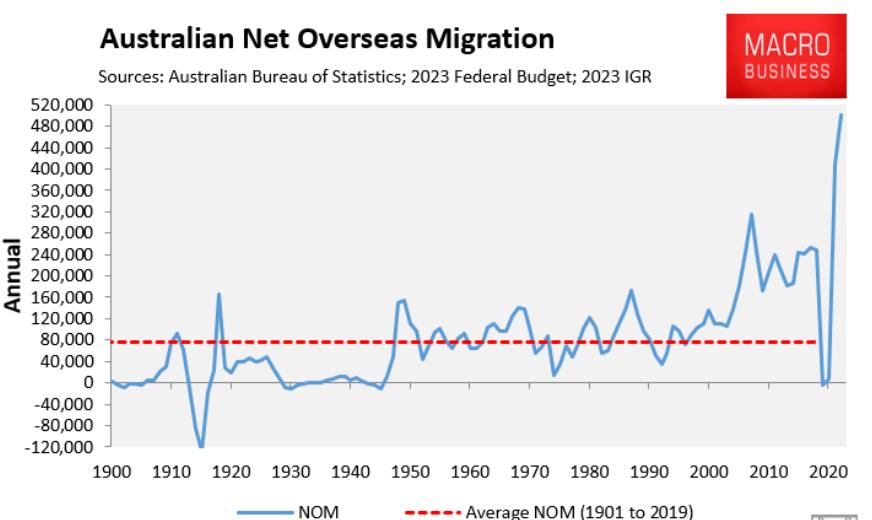
Labor Force Participation Rate Graph
Let’s discuss some individual countries and regions. First, take a look at the above labor force participation rate graph. It shows the number of people either looking for work or who have work. Can you tell that there were a few good months? That’s how good the American economy is after your few good months. It didn’t really improve much, it just went horizontal.
You need a few years of such job results to make a difference. And that’s before we get to the fact that most of those jobs were low-paying and that all of the gains of the last economic cycle have gone to the top three to five percent of the population (depending on how you slice it). And the top 1% has done better than 3%, the top .1% better than the top 1% and so on. This is your economy on unconventional monetary policy.
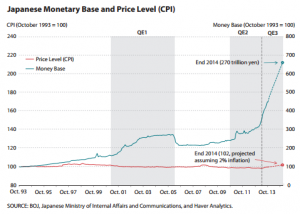
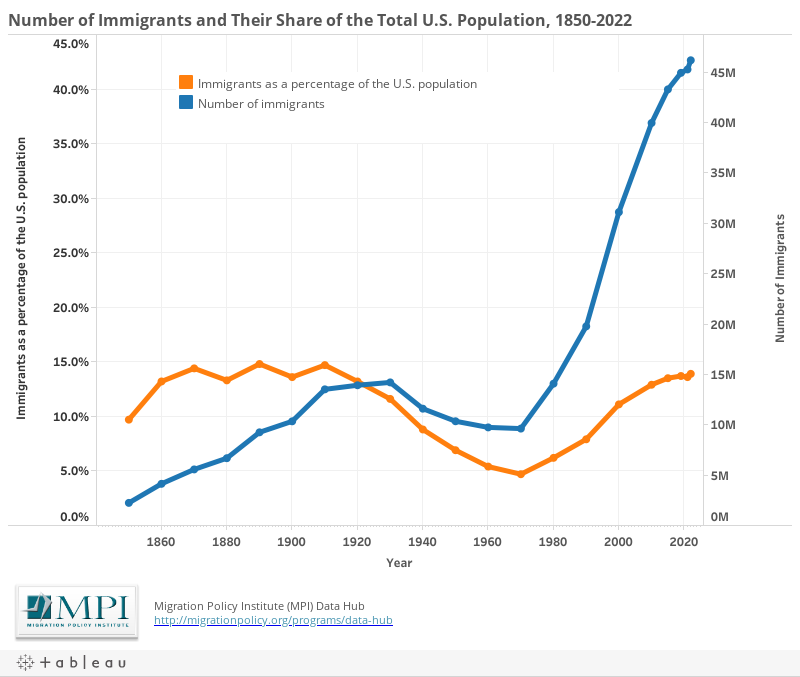
Japanese monetary base and inflation to early 2015
Ah, unconventional monetary policy. In Japan they call it “Abenomics.” The idea was to get inflation going in the Japanese economy–get the Japanese to spend and bring Japan out of its 30 year slump. The chart to the right shows how well it has worked.
But don’t think that money has been “wasted!” Abenomics may have done nothing for ordinary people, but it’s helped a lot of rich people become richer. That money went somewhere. In Japan’s case, a ton of it will have gone overseas, with foreigners borrowing for low costs in Japan and then speculating with that money elsewhere for higher gains (or so they hope).
Unconventional monetary policy is, and always has been, about giving money to the rich, wealthy, and corporations. At first, it was about bailing them out after the financial collapse. Now, it’s just about giving them money, lots of money, in a way that the hoi-polloi can’t access.
This brings us to Europe and austerity. Austerity is a wonderful thing, if you’re rich. Public assets are put on the selling-block which you normally could never buy and they are put there for cheap. You get to own more of the economy, your relative wealth increases. While it’s true that one might be richer in a generally prosperous economy, you must remember, this isn’t about absolute wealth. It’s about relative wealth. Better to be somewhat poorer and able to lord it over everyone else, than be richer in a world where the peons don’t have to kowtow to your every whim or don’t have to live miserable, want-filled lives. If the price is a lot more poverty, that doesn’t affect you in any meaningful way.
Not all peons suffer, of course. A lot of Germans do very well in the current regime. As the South of Europe suffers under austerity, they’re doing great. The worse the southern economies are, the better for Germany, since it reduces the price of the Euro, increasing German exports. If everyone in the Euro area was doing well, Germans wouldn’t be doing nearly so well. If the price is suicides, widespread poverty, homelessness, and so on, that’s certainly a price Germans are willing for Italians, Spanish, Greeks and Portuguese to pay.
Meanwhile in Canada, there is a housing bubble which kept on going from the point where the US bubble collapsed. Better, inflated prices are guaranteed by the Federal government, so when the bubble bursts, it can cause maximum damage to public finances. With oil prices falling, and with Canada now a petro-state (as I noted almost a decade ago) due to deliberate government policy, those housing prices are looking less and less sustainable.
In the UK, we also have London’s housing bubble (which is to say, the majority of the actual economy of the UK, if you want to call a housing bubble and financial services an economy, which UK politicians do). This shouldn’t be a surprise, since the UK hired Canada’s ex-central banker to come to the UK and do what he did to Canada: Blow a nice big bubble. The UK hardly has any other economy besides real estate and financial ponzi schemes, so we’ll see how that works out for them.
In general, understand this: The world bailed out bankers and brokers and traders and they went back to doing what they were doing before. Blowing bubbles. There are CDOs out the wazoo, there are stock market bubbles, there are real-estate bubbles in various places (they just tend to be more localized now, but they’re still huge).
The economy will NEVER be good for everyone until this is changed, but that doesn’t precisely mean this is unsustainable. The elite’s had one fundamental realization and it was this:
“We can print as much money as we want and as long as we make sure it doesn’t get into ordinary people’s hands it won’t blow up the economy.”
Many people expected that unconventional monetary policy would cause general inflation. It hasn’t because the money stayed in the hands of a very few people and major corporations. It did cause massive inflation in the things rich people buy, but not general inflation.
So the rich, and the politicians and central bankers they own, aren’t worried about the various bubbles because they handled them in 2007 and 2008, and they’re sure they can handle them the same way if they burst again. These bubbles may never all burst at the same time again, because if they show signs of doing so, the elites can always just have the central banks print money and buy up assets before they even become distressed.
As long as there is no actual price discovery (and how can there be), there is no real threat to the only part of the economy that matters: The economy of the people with enough money buying up politicians.
Everyone is addicted to this game, even China, which has printed unbelievable amounts of money (more than Japan, America and Europe combined) and has used it to create vast amounts of unused and unusable housing and other boondoggles. China, granted, wants much of the benefits to get to ordinary people (because the Chinese are still willing to riot extremely violently and the Communist party’s leadership knows their lives are on the line), but they’re still playing the late-capitalist game of credit pumping, rather than the mercantilist game which built the Chinese economy. That makes sense, in a way. As China’s customer-economies stagnate, it becomes harder and harder to create widespread growth for the most populous country in the world through simple exports.
The correct strategy would be to start decoupling and move to a domestic market, and in a sense, the Chinese have tried that, but they’ve bungled it on boondoggles. Capitalism of the variety we do today is terrible at redistribution and redistribution is what the Chinese economy needs, in a huge way, in order to boost widespread demand.
So that, my friends, is your world economy on austerity and unconventional monetary policy. As I predicted right after Obama put out his worthless “stimulus” program in early 2009, for most people, the economy will not recover for at least a generation. It will only recover then if the population is willing and able to rebel, peacefully or violently. If not, we are in for decades of stagnation and decline, exacerbated by the absolute certainty of catastrophic climate change.
And so it goes…
If you enjoyed this article, and want me to write more, please DONATE or SUBSCRIBE.