There’s been a lot of hysteria over the ballooning US deficit lately. Is it worth worrying about? Let’s learn how you can tell for yourself, rather than relying on others to tell you.
This is the sort of chart which is going around:
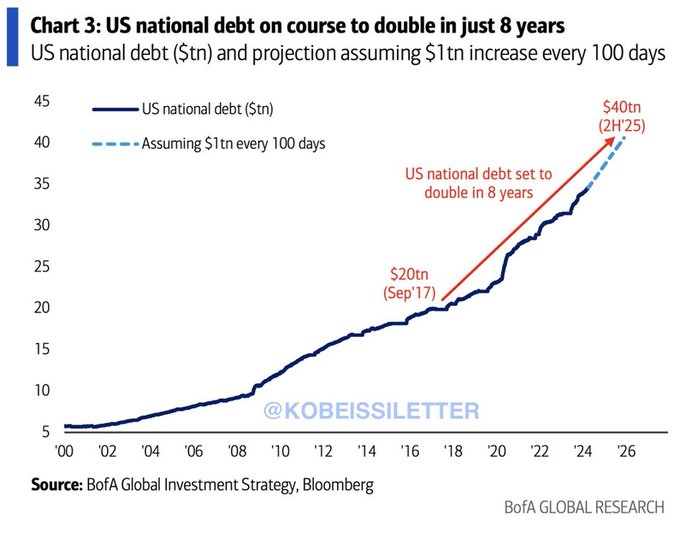
Scary, eh?
So, here’s the debt long term, as a percentage of GDP:
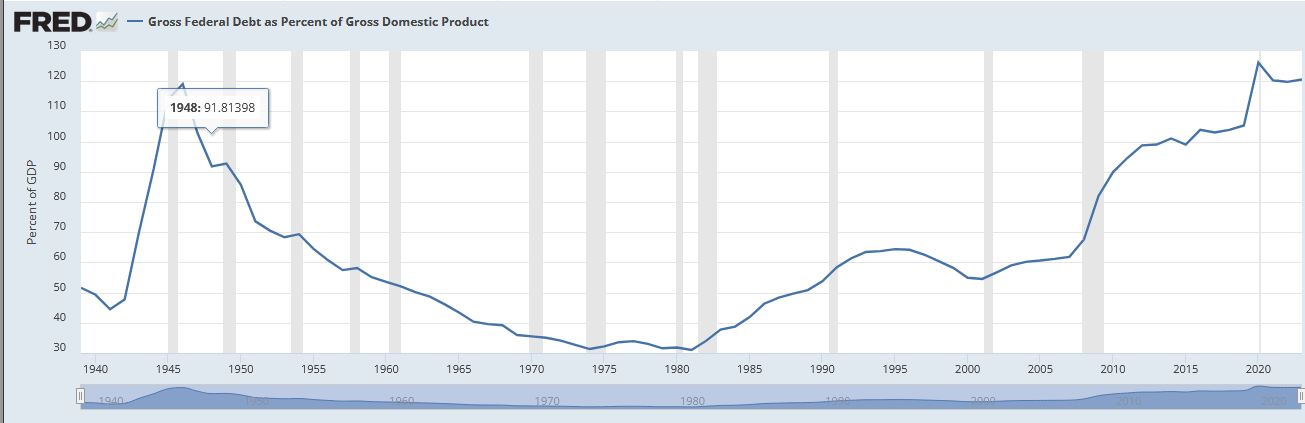
Still pretty scary. US debt it is running higher than WWII debt.
In the short run, most of this is caused by interest payments:
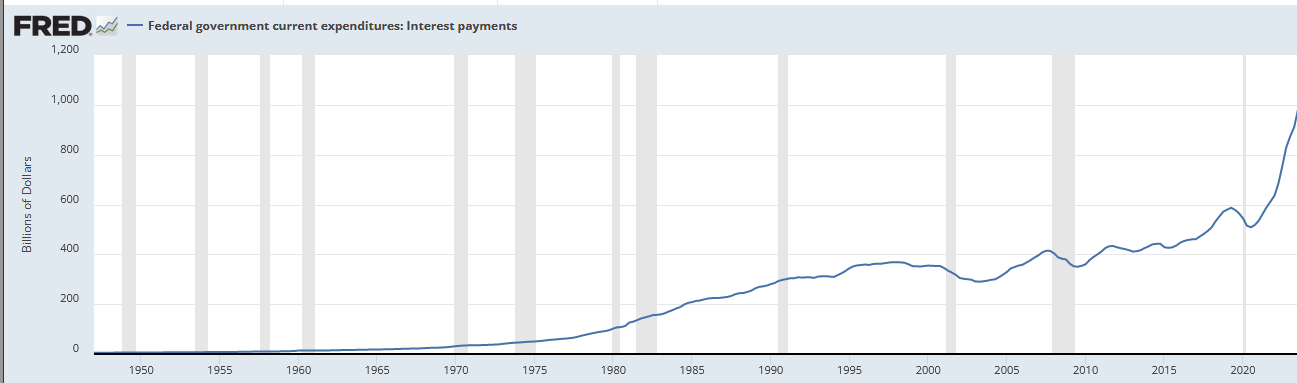
So, what changed? Prime.
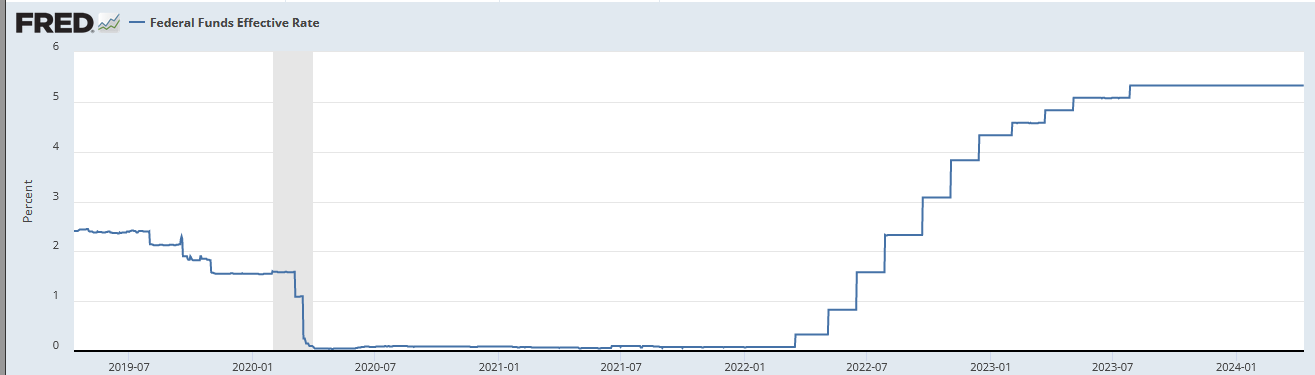
If you take a look at these charts you’ll see the rise in rate of increase is mostly due to interest.
Now, when governments who can print money default, it is because people don’t want their money, or the money can’t buy what what they need. US debt is entirely in US dollars. Treasury can mint as many bonds as it likes, and the Federal Reserve can buy them. It is impossible for the US federal government to run out of money, per se.
Rule: Debt is a problem for a government with the power of the printing press when money can’t buy what is needed.
Regular readers will know I am fond of Keynes maxim: “Anything we can do, we can afford.”
The corollary is “Anything we can’t do, we can’t afford.”
It doesn’t matter how much money you have. You can’t build a nuclear bomb in 1900. You can’t build a nuclear bomb if you are Nicaragua. For ages no one but the US and Europe could, effectively, build commercial airliners. You can’t buy what you can’t produce.
In 1945 the US debt did not matter. The US was half the world’s economy, and everything it needed to produce, including oil, it produced itself. It also had the power of taxation: the top marginal rate was 94%.
Rule 2: Money can’t buy what you need when you can’t produce it and those who can produce it won’t sell it to you.
Right now the US cannot produce much of what it needs. It does have a food surplus and can survive on its own domestic food production and it has a surplus of petrochemicals BUT much of the goods it genuinely needs, like basic electronics and production equipment are no longer made in America.
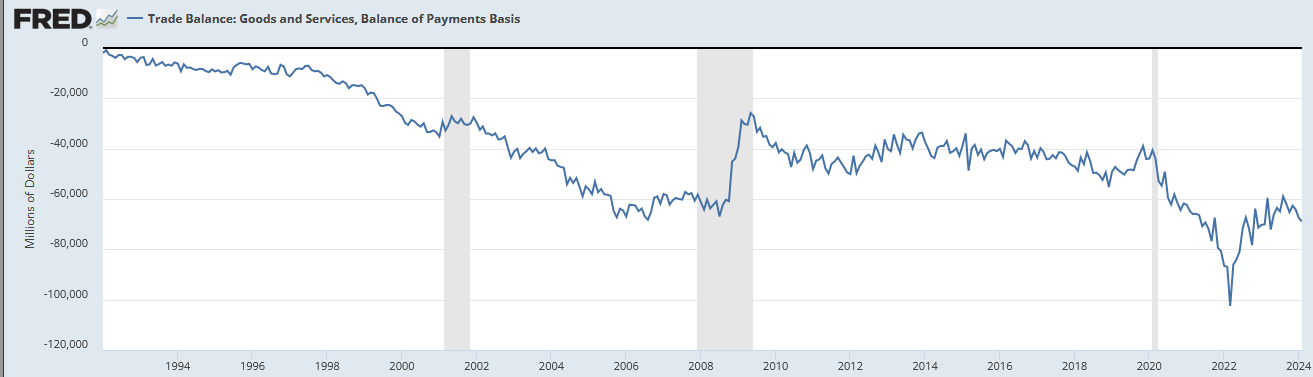
Let’s look at three charts. First the trade deficit in goods and services:
Now, let’s look at the trade balance in services:
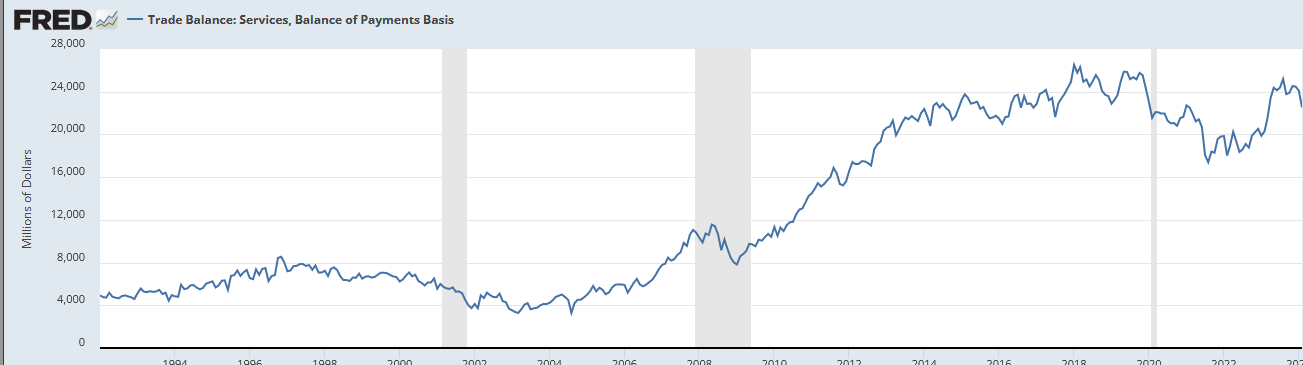
So, the US has a trade surplus in services. Crap like intellectual property and management consulting. Stuff people can do without if they must or can ignore if they choose.
Now, trade balance in goods:
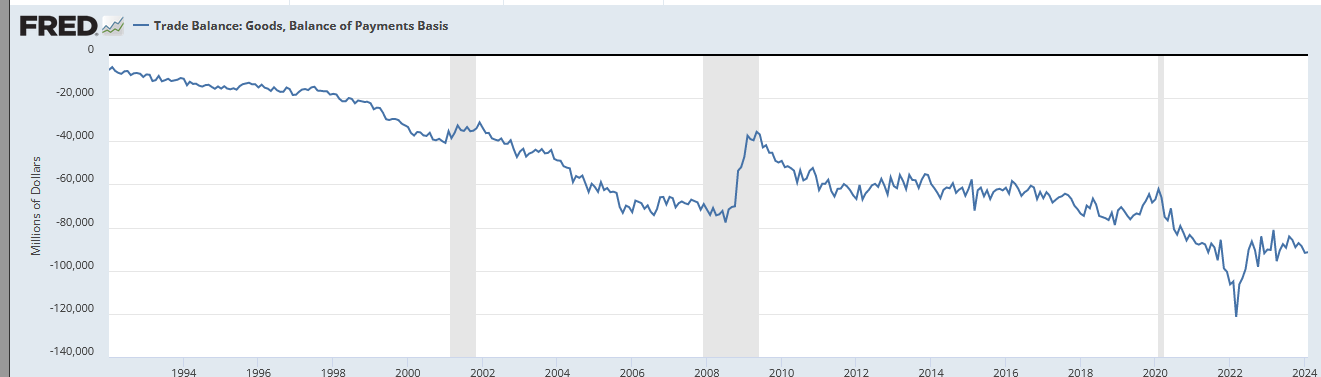
The trade balance in goods is what the US doesn’t make itself that it wants or needs. Some of it is crap: you don’t need summer vegetables in the winter. Nice to have, but not needed. But a lot of it is important: those basic electronic and mechanical goods, including production goods which the US no longer makes and in many cases no longer knows how to make.
The overall trade balance doesn’t look so bad, but it is made to look way better than it is by the US trade surplus in services, which are far less important than goods.
When the US can’t make or buy what it needs using US dollars the deficit matters.
That means the key point is when other countries stop taking US dollars as default. When the dollar is no longer the medium of trade. Right now almost everything can be bought in dollars, which the US can print. If and when that changes, the US is up shit creek without a paddle.
But there is another set of issues: domestic ability to pay.
Specifically, when you can’t pay the enforcer class. Cops and military and judges and prosecutors and prison guards and all that security crap.
America is a vastly unequal society, seething with latent unrest. If the people who protect the status quo won’t fire, then the government and the peace is at great risk. We say this during the January 6th insurrection: most of the capital cops were not willing to fire. This was an ideological issue: they were sympathetic to right wing protesters, just as cops tend to protect Nazis and beat down socialists and blacks.
But it can also become a financial issue. You can print as much as you want, but if people can’t buy what they need with it, it’s worthless. See Weimar Germany hyper-inflation. Or you can refuse to pay, because part of the ruling coalition wants too much of the money and won’t give it to others. Most of the policing in the country is local: it is financed by states and municipalities which do not have the power of the printing press and which do not have a great deal of effective taxation ability: people and business can leave the state or the municipality, in addition to the normal elite capture rule.
When the Bolsheviks took over Russia, most of the enforcer class was not being paid, or couldn’t buy what they needed with the money they were being paid. So when push came to shove, they didn’t fight for the government, and many (especially the navy), switched sides.
Likewise, as Lenin observed, ordinary people are genuinely willing to violently revolt when the risk of doing so is less than the risk of not doing so.
The key question, then, is inflation. Unfortunately, in the US and the West in general, actual inflation is impossible to tell thru official stats. You have to judge buy your own grocery bill; your own fuel bill and your own expenses, and those of people you know. Do you and others have excess money to spend?
Inflation spikes when there isn’t enough to go around. It’s that simple. If a country can’t produce what it needs or wants, and others start raising their prices or refusing to sell, inflation becomes a problem.
Even without inflation, decreasing surplus income is a problem. This is why inequality matters: if a large chunk of the population can’t buy what they need, well, Lenin’s maxim comes into play.
China is at risk of deflation (not significant risk, yet, but that’s their danger.) The US and Europe and the Anglosphere are at risk of inflation.
That inflation will happen when others won’t or can’t sell us what we need and we can’t make it or grow it or mine it.
It is at that point where the US deficit will matter.
If you want to know when the US deficit will matter, it’s simple: when China and other countries stop using dollars as the default trade currency. That process is early yet, but underway. It used to be unthinkable to sell oil in anything but dollars: did not happen. Now it does. China and Russia, China and India, and Iran and everyone now trade without dollars. African countries are in the midst of throwing out French and American military bases and do the majority of their trade with China, not America or Europe. They are increasingly trading with Russia, as well, and relying on it for military aid.
Everything those countries need except for some medicine they can get from Russia and China: food, goods, and fuel. China gives them better debt terms and doesn’t interfere in most countries internal politics nearly as much as America does.
This is the actual threat: the West not being able produce what it needs and other countries no longer willing to accept dollars. Track this by watching actual inflation, and observing the process of global de-dollarization.
The deficit and the debt don’t matter much, yet.
But they will.
You get what you support. If you like my writing, please SUBSCRIBE OR DONATE